In this page, you will learn about how to implement Appbase.io analytics for your stack and use-case.
Prerequite: Deploying Appbase.io
Appbase.io Analytics requires a deployment of appbase.io alongside your Elasticsearch cluster. You can deploy appbase.io as:
- A hosted offering: (Recommended) for a complete end-to-end managed experience. Learn More
- Deploy as a Docker image: Run anywhere, including with your Kubernetes Elasticsearch cluster. Learn More
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI): Deploy within your VPC alongside AWS Elasticsearch. Learn More
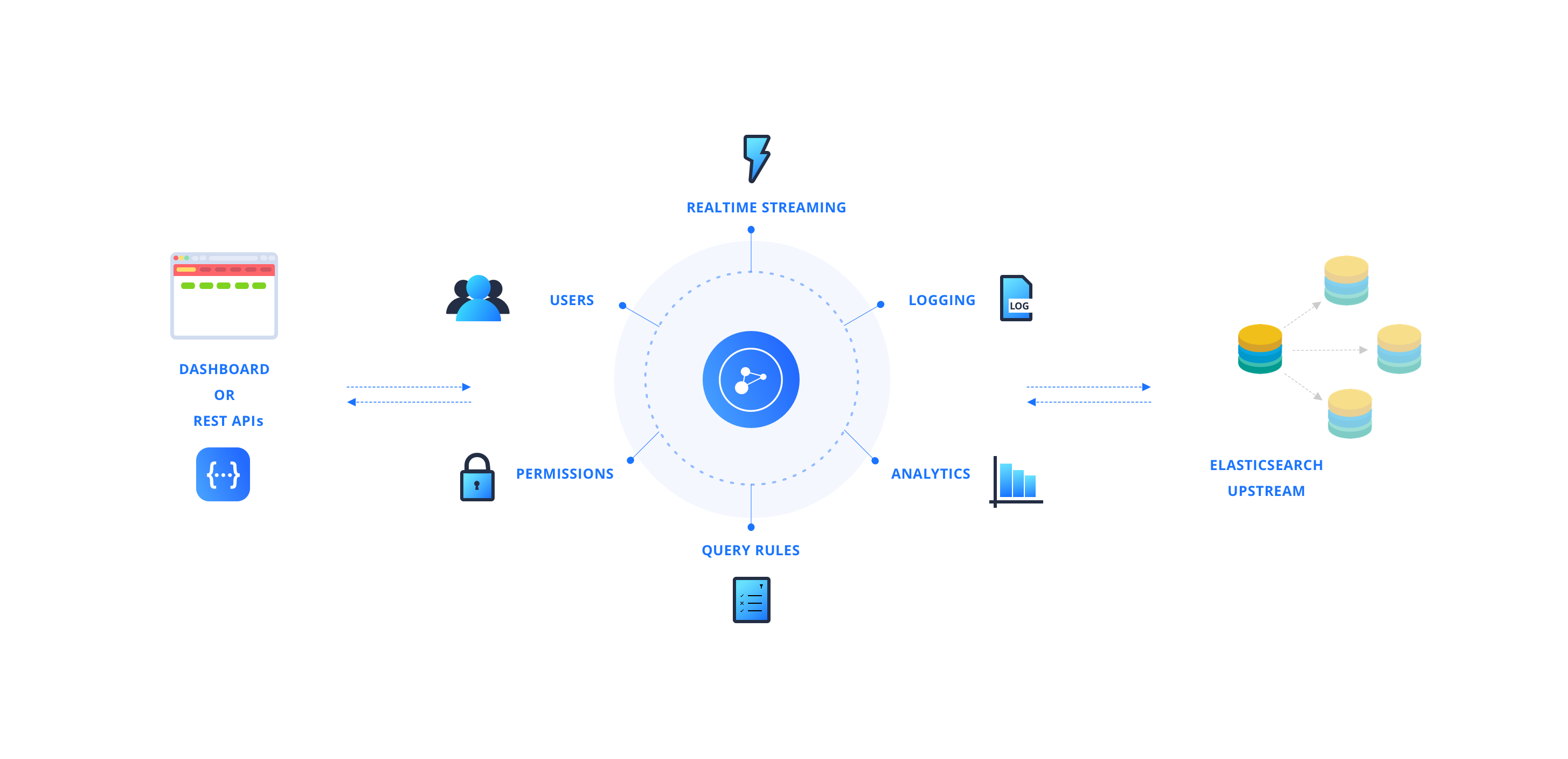
How To Track Analytics
Appbase.io offers turnkey search analytics for Elasticsearch. No matter how your search is implemented today, it's easy to integrate analytics in a matter of minutes.
With Appbase.io UI Libraries
If you're already consuming any of the below libraries to build your search UI, then you don't need any additional setup. These libraries support a prop called analytics which when set to true enables the recording of search analytics. They also come with additional configs to track custom events. You can go to the specific library that you're using to learn more.
Library |
Variant |
Docs |
|---|---|---|
ReactiveSearch |
React |
Learn More |
ReactiveSearch |
Vue |
Learn More |
SearchBox |
VanillaJS |
Learn More |
SearchBox |
React |
Learn More |
SearchBox |
Vue |
Learn More |
SearchBox |
React Native |
Learn More |
SearchBox |
Flutter |
Learn More |
SearchBase |
VanillaJS |
Learn More |
SearchBase |
Dart |
Learn More |
With any JavaScript
If you're not using any of the above search UI libraries or need more freedom to record clicks and conversions from any place in your application, then we recommend using analytics.js. Analytics.js can be used to integrate Appbase.io analytics with any JavaScript based solution (client or server) and it covers all aspects of Appbase.io analytics from recording a search event to recording custom events and clicks. You can read more about it here.
With REST API
Analytics REST APIs allow you to record search and click analytics from any platform (mobile, server-side) of your choice.
There are three types of analytics:
- Search Analytics,
- Click Analytics and
- Conversion Analytics
1. Search Analytics
Use PUT /:index/_analytics/search endpoint to record a search event.
curl --location --request PUT 'http://{{USERNAME}}:{{PASSWORD}}@{{CLUSTER_URL}}/{{INDEX}}/_analytics/search' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query": "iphone",
"user_id": "jon_snow",
"event_data": {
"platform": "mac"
},
"filters": {
"year": "2018"
},
"hits": [{
"id": "12345678",
"source": {
"title": "iphoneX"
},
"type": "_doc"
}]
}'API reference over here.
2. Click Analytics
Use PUT /:index/_analytics/click endpoint to record a click event.
curl --location --request PUT 'http://{{USERNAME}}:{{PASSWORD}}@{{CLUSTER_URL}}/{{INDEX}}/_analytics/click' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query_id": "89c14471-2df5-4414-8b17-33479ef71bc0",
"click_type": "suggestion",
"click_on": {
"iphone_1234": 2
},
"user_id": "kuldeep-2",
"event_data": {
"user_segment": "paid"
}
}'API reference over here.
3. Conversion Analytics
Use PUT /:index/_analytics/conversion endpoint to record a conversion event.
curl --location --request PUT 'http://{{USERNAME}}:{{PASSWORD}}@{{CLUSTER_URL}}/{{INDEX}}/_analytics/conversion' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query_id": "e3840c97-dd30-4696-8781-f355f40dd0f4",
"conversion_on": [
"iphone_1234"
],
"event_data": {
"user_segment_2": "free"
}
}'API reference over here.
Note:
Recording custom events is available as an enterprise feature. You need to have at least
Production-Iplan or anArc Enterpriseplan to avail this.
Appbase.io Apps
If you are using appbase.io apps (legacy), you can implement analytics in the following manner:
Search Analytics
When using the REST API to make a search query, you can pass along the following headers:
X-Search-Query -> The value here represents the search query term (the input value in SearchBox if you are using ReactiveSearch).
Whenever an X-Search-Query header is passed, the API returns a response header for the search Id called as X-Search-Id. This can be passed further as a request header to associate other search attributes (filters, clicks) with the same original query. Think of X-Search-Id as a search session.
X-Search-Id -> An existing Id (aka search session) on which to apply the search query. This is returned as a response header by the backend for each search query.
X-Search-Filters -> This header should contain the value in the format: "key1=value1,key2=value2,..." where the key represents the filter component and value represents the selected value. (If the same filter has multiple values selected, they should be passed as "key1=value1,key1=value2,...").
Click/Conversion Analytics
There is a POST /:app/_analytics endpoint which can be used to record click analytics.
For example:
curl --location --request POST "https://scalr.api.appbase.io/{APP_NAME}/_analytics" \
--header "X-Search-Id: replace-with-real-search-id" \
--header "X-Search-Click: true" \
--header "X-Search-ClickPosition: 5" \
--header "X-Search-Conversion: true" \
--header "Authorization: replace-with-basic-auth-credentials"The above endpoints accept the following values as headers:
X-Search-Click -> value is of type true / false,
X-Search-ClickPosition -> value is of type Number (e.g. 1, 2 denoting the result item being clicked)
X-Search-Conversion -> value is of type true / false.
Advanced Settings
How To Enable / Disable Empty Query
By default, a library such as ReactiveSearch shows you a set of initial results even when no search query has been explicitly performed. The initial results are displayed by calling a match_all query which can be considered as an empty query. By default, we record the analytics for empty queries too. You can find out about it in the Appbase.io dashboard with the <empty_query> key.
You can disable this behavior in ReactiveSearch by defining the appbaseConfig prop in the ReactiveBase and set the emptyQuery as false.
How An Analytics Session Works
An analytics session is driven by the X-Search-Query header or query field if you're using the REST API. It is the user's responsibility to define the search query to trigger an analytics session. One analytics session can be considered as one search count.
Don't worry! ReactiveSearch handles this for you. You just need to set the analytics prop as true in the ReactiveBase component. Read more about how to configure analytics in ReactiveSearch.
How Are Searches Counted
- When a user types something in sequence, for example:
b→bo→boo→book, we understand the context and instead of creating different search sessions, we count it as a search session with search key stored asbook. - By default, the search context is valid for up to
30s. For example,b→bo→boo...30 seconds...->bookwill be recorded as two different searches with keys asboo&book.
How Do We Record A User Session?
- A user session starts when an end-user makes a search request from a web or mobile device.
- A user session is kept active for up to 30 minutes after the last user interaction. For example, if a user closes a tab and comes back within 30 minutes - the old session is kept active instead of another session getting created.
- However, when accounting for the session duration, appbase.io uses the user's last interaction time as the end time.
Let's take an example scenario:
=> Bob made the first search request at 10:00. At this point, a new user session got created for Bob which will remain active till 10:30,
=> If Bob makes a click, applies a filter or searches again at 10:05, then the active session time will be extended till 10:35 and the session duration will be recorded as 5 mins (last interaction time 10:05 - session start time 10:00).
- A user session is made unique by the
userIdkey which defaults to the IP address of the end user. A change in theuserIdof the search request will start a new session.
How Is The Bounce Rate Calculated?
In the context of appbase.io search analytics, a session is marked as bounced when a user visit the search page (the page which makes at least one search query to appbase.io) and then leaves the session without making any further interactions.
An interaction is defined as:
- A new search request with a different search term, for example, a user visited the search page and then searched for
books, - A click is made on
suggestionsorresults, - A new filter (aka facet) has been applied on the search,
- A page is changed.
If any one of these interactions happen, then the session is not considered as a bounce session. The bounce rate is then defined as the percentage of user sessions that have bounced relative to the total user sessions.
Bounce Rate = ( Total
bounceduser sessions / Total user sessions ) * 100
Bounce rate helps you to understand how engaging your search experience is. If you are seeing a higher bounce rate, it's time to tweak your search relevancy settings.



